
11.º Q2.1. Reações ácidobase pH pOH Kw [H3O+] [OH] Resolução exercícios YouTube
2 years ago It's just Kw at 25°C. It's a constant which is found in any chemistry textbook's data tables. ( 5 votes)
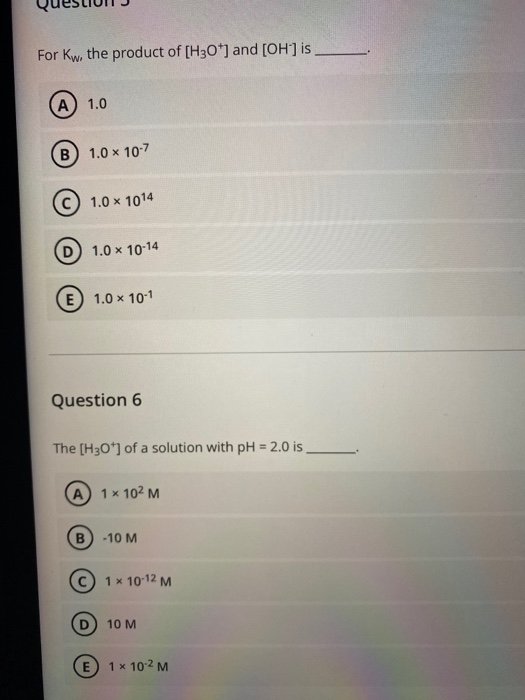
Solved For Kw, the product of [H3O+] and [OH] is A) 1.0 B
Re: Kw and H3O/OH concentrations. Postby 805422680 » Tue Jan 14, 2020 7:34 am. the Kw of water remains constant at a given temperature, although the concentrations of hydronium and hydroxide ions can vary. for example, in an acidic solution if [H3O+] is say 1.00 x 10^-2, then using the Kw, we can conclude that the [OH-] is 1.00 x 10^ -12. Top.

pH, pOH, H3O+, OH , Kw, Ka, Kb, pKa and pKb Basic Calculations of Acids and Bases Chemistry
2 years ago It is conventional to omit pure liquids (like water), solids, and solvents from equilibrium expressions. This is a consequence of exactly how each quantity is defined.
PPT Acids and Bases PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5408038
This acids and bases chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into the calculation of the pH and pOH of a solution. This video explains how to.

Solved Use the following relationships to solve the problems
CHEMISTRY COMMUNITY Tweet H3O+ and OH- from Kw Moderators: Chem_Mod, Chem_Admin 3 posts • Page 1 of 1 Belinda_Ho_2L Posts: 50 Joined: Fri Sep 29, 2023 5:55 pm H3O+ and OH- from Kw Postby Belinda_Ho_2L » Fri Jan 19, 2024 11:25 pm How do you find H3O+ and OH- concentrations from Kw?

16 3 Kw and H3O and OH YouTube
3O+ and OH-•for any aqueous solution [H 3O+] [OH-] = a constant •if one increases, the (other decreases •Kw = 1 x 10. (aq) + OH-(aq) For any aqueous solution [H 3O+]] [OH-] = an EQ constant called Kw The value of Kw is 1.0 x10-14 Kw = 1 x 10-14 = [H 3O+] [OH-] [H 3O+] = [OH-]= April 28, 2014 Recall, a strong acid ionizies 100% in water.

PPT Acids & Bases PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1994749
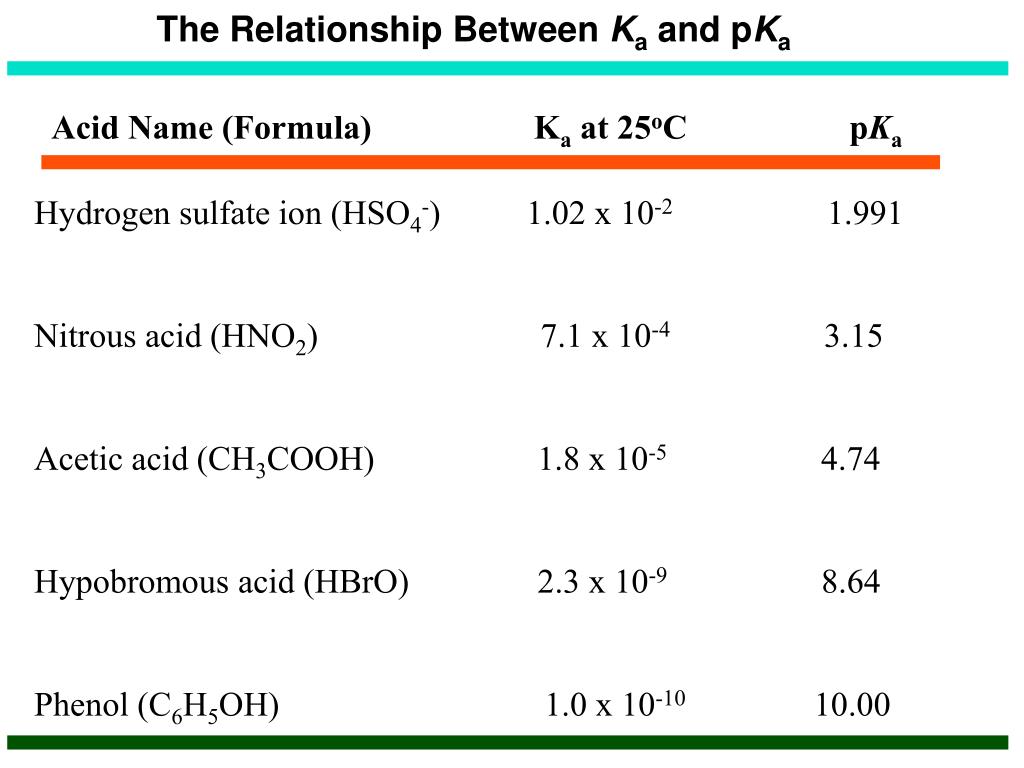
Since H3O is one of the products due to HCl donating its hydrogen proton, we use the Ka value of HCl in our equation. Ka = (1.3 * 10^6) = [H3O] [Cl] / [HCl] Similarly, if a reaction yielded an OH-* ion, then we'd use the *Kb (base-dissociation constant) value in our equation. Keep in mind that Kb = Kw/Ka :)

PPT Chapter 10 Acids and Bases PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4509587
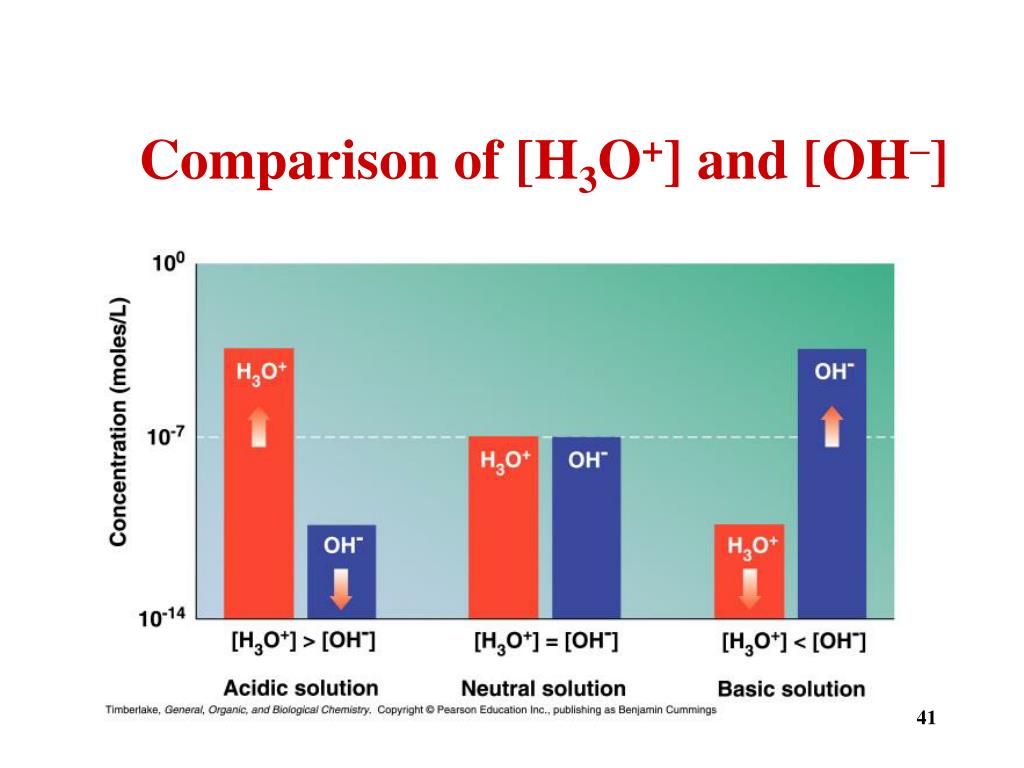
. In a neutral solution, [ H 3 O +] = [ OH −] In an acidic solution, [ H 3 O +] > [ OH −] In a basic solution, [ OH −] > [ H 3 O +] For aqueous solutions at 25 ∘ C , the following relationships are always true: K w = [ H 3 O +] [ OH −] = 10 − 14 pH + pOH = 14 The contribution of the autoionization of water to [ H 3 O +] and [ OH −]

Calculating [H3O+] and [OH] Using Kw Guided Practice 1 YouTube
Then you convert it to pH. In pure water at room temperature the K w value tells you that: [H +] [OH -] = 1.00 x 10 -14. But in pure water, the hydrogen ion (hydroxonium ion) concentration must be equal to the hydroxide ion concentration. For every hydrogen ion formed, there is a hydroxide ion formed as well.

PPT POWER POINTPRESENTATION ON IONIC EQUILIBRIUM AND CONCEPT OF pH PowerPoint Presentation
The relationship among pH, pOH, and the acidity or basicity of a solution is summarized graphically in Figure 16.3.1 16.3. 1 over the common pH range of 0 to 14. Notice the inverse relationship between the pH and pOH scales. For any neutral solution, pH + pOH = 14.00 (at 25°C) with pH=pOH=7.

Chapter 16 Lecture Acid/Base Equilibrium
The product of the molarity of hydronium and hydroxide ion is always 1.0 ×10−14 1.0 × 10 − 14. Kw = [H3O+][OH−] = 1.0 ×10−14 (12.5.2) (12.5.2) K w = [ H 3 O +] [ O H −] = 1.0 × 10 − 14. This equations also applies to all aqueous solutions. However, Kw K w does change at different temperatures, which affects the pH range.

2H2O H3O^+ + OH^,Kw = 1 × 10^14 at 25^∘C . Hence, Ka is
The equilibrium of water is described with the equation: K=[H3O+][OH−][H2O] Where K is the equilibrium constant equal to the concentration of products over the concentration of reactants. The ion concentrations of hydronium and hydroxide are equal to each other at standard temperature, 25°C, [H3O+]=[OH−]= 1.00 x 10−7.

Calculate [H3O+] and [OH] using Kw McMurry CH14 Problem 55 YouTube
About Transcript Strong bases (such as Group 1 and 2 metal hydroxides) dissociate completely in water to produce hydroxide ions. The concentration of OH⁻ in a strong base solution can therefore be determined from the initial concentration of the base and the stoichiometry of the dissolution.

Chem 309 Acids & Bases Part 5 Kw H3O+ & OH Calcs YouTube
Kw Chemistry November 23, 2017 Introduction to the water ionization constant K w Pure water undergoes auto-ionization or self-ionization by donating or accepting a proton between two molecules of water to form H 3 O + and OH - ions. This is also known as autoprotolysis or amphoteric nature of water.

PPT Acid and Base Equilibrium PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3206252
(H3O+)(OH-) (H2O) **This is a legal and useful approach. Remember, the K is an algebraic, numerical constant. Because the activity of water is 1: KaKb = (H3O+) + (OH-) = Kw = 10-14 Where Kw is the equilibrium constant water. This relationship allows the calculation of either Ka or Kb if the other is known by: pH + pOH = pKw = 14
PPT Chapter 10 Acids and Bases PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4509587
To calculate the Kw, we determine the concentration of hydrogen and hydroxide ions in pure water at room temperature. The value of Kw at 25°C is 1.00 X 10-14 mol2dm-6. We can also calculate ph from Kw. Since the concentration of H+ ions and OH- ions in pure water is the same, the concentration of each of these ions is the square root value of Kw.